The CPSC recently announced its first civil penalty of 2021. Cybex International, Inc. (Cybex) agreed to pay $7.95 million after the workout equipment manufacturer allegedly failed to immediately report to the CPSC the defects in two of its products.
The first product was an arm curl machine, which had a defective weld that could cause the machine’s handle to separate unexpectedly and strike the consumer in the face. Cybex received 85 reports of broken handles, including one report of permanent vision loss, but allegedly failed to immediately report the defect to the CPSC. Cybex eventually recalled the arm curl machines in August 2015. The second product was a smith press machine, whose weight bar could fall and strike the consumer. Cybex received 27 reports of fallen weight bars, including reports of paralysis and spinal fracture, but allegedly failed to immediately report the defect to the CPSC. Cybex eventually recalled the smith press machines in August 2018.
In addition to paying the civil penalty, Cybex agreed to maintain an enhanced compliance program for the CPSC, as well as a system of internal controls and procedures, to ensure information required to be disclosed to the agency is recorded, processed, and reported. Of the four CPSC Commissioners, three voted to approve the civil penalty agreement (Acting Chairman Adler and Commissioners Kaye and Baiocco) and one did not vote and, therefore, was considered to have abstained (Commissioner Feldman). After a hiatus from civil penalties, this is the second recent CPSC civil penalty, with the other announced in December. Perhaps these recent developments indicate the return of the civil penalty as a more regular enforcement tool of the agency.
The CPSC also recently released a report during National Consumer Protection week that quantifies hospital emergency room-treated injuries from consumer products during the COVID-19 pandemic from March through September 2020. The report observed large increases in ER-treated injuries across all age ranges for fireworks and flares (56%); skateboards, scooters, and hoverboards (39%); all-terrain vehicles including mopeds and minibikes (39%); cleaning agents (84%); and soaps and detergents (60%). Hoverboards, as well as all-terrain and recreational off-highway vehicles, have been recent regulatory focuses of the CPSC. We expect to see other consumer product categories emerge as regulatory focus areas for the CPSC in the coming months.
Lawyers from Hunton Andrews Kurth LLP’s insurance coverage practice provide an update on a recent food contamination-related insurance coverage dispute tied to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic:
In a setback for retail-policyholders hoping to enforce coverage for losses due to COVID-19 in federal court, a Tennessee district court recently knocked out a complaint filed by a sprawling Nashville establishment seeking coverage under a food contamination provision in its property policy. The court’s opinion dismissing Nashville Underground LLC v. AMCO Insurance Co. is noteworthy due to the great lengths taken to define a policy provision regarding coverage related to food contamination. The provision is intended to provide broad coverage for disruption of business due to the suspected food contamination by limiting coverage contrary to the reasonable expectations of businesses that purchase policies specifically tailored to protect against actual or suspected contamination.
Nashville Underground LLC—“nationally acclaimed, seven-story restaurant, bar, night club and live music venue” located in downtown Nashville—procured a commercial property policy from AMCO Insurance Company (AMCO) to protect it from fortuitous catastrophic events. Given the heightened risk to its business posed by a disruption stemming from food contamination, Nashville Underground purchased a special coverage for business interruption due to “Food Contamination.” Specifically, the policy would provide business income coverage if Nashville Underground was shut down by a governmental authority as a result of the “discovery or suspicion” of “an outbreak of . . . food-related illness of one or more persons arising out of . . . [f]ood which has been contaminated by virus . . . transmitted through one or more of [its] employees.”
In March 2020, COVID-19 spread rampantly across the country. In an effort to stop its spread, local governments issued broadly worded orders admonishing the public to stay home and requiring non-essential businesses to close. Under the orders issued in Nashville, Nashville Underground was required to close, cutting off all of its income. When Nashville Underground sought coverage under its policy, AMCO denied the claim.
Nashville Underground sought to enforce the coverage it paid for by filing suit in Tennessee state court, and AMCO removed the case to federal court. Despite Nashville Underground’s allegations that the government orders requiring its closure were issued in part due to suspicion that COVID-19 was spread through contamination of food and that its employees were exposed to COVID-19 potentially contaminating the food served at Nashville Underground, and despite the lenient notice-pleading standard applicable in federal courts, the court dismissed the complaint.
The thrust of the court’s determination was that the Food Contamination provision was triggered “only if there is suspicion of one or more particular persons actually having become ill,” as opposed to a suspicion that a food-related illness may occur in the future, because the relevant policy wording is written in the “past tense or present perfect tense.” According to the court, coverage under the Food Contamination provision applies only in the limited circumstance where a business is shut down by government order due to a suspicion of an outbreak of food-related illness following confirmed cases of individuals getting sick due to food contaminated by employees. In other words, the prophylactic closure of a restaurant pursuant to mandatory government orders aimed at preventing an outbreak of suspected food-related illness transmitted by food-handlers is not covered.
However, the court’s narrow interpretation is hard to square with what the average policyholder would expect when procuring coverage for business interruption due to food contamination, irrespective of the “tense” used in the language. Indeed, it is hard to imagine a restaurant owner discerning any meaningful difference between a government order that shuts down a business due to suspicion that contaminated food may get people sick and a suspicion that contaminated food has already gotten people sick. To the restaurant owner it is all the same—his or her business must close due to “suspicions” of food contamination. And, therefore, it was incumbent upon the insurer to clearly state that the coverage only applied if people got sick first, which it plainly did not do.
The Nashville Underground case admittedly presents a unique issue among the many COVID-19 related coverage lawsuits pending throughout the country. Unfortunately, it is consistent with the same strained interpretations of policy language adopted by federal courts in limiting broad grants of coverage for the COVID-19 pandemic.
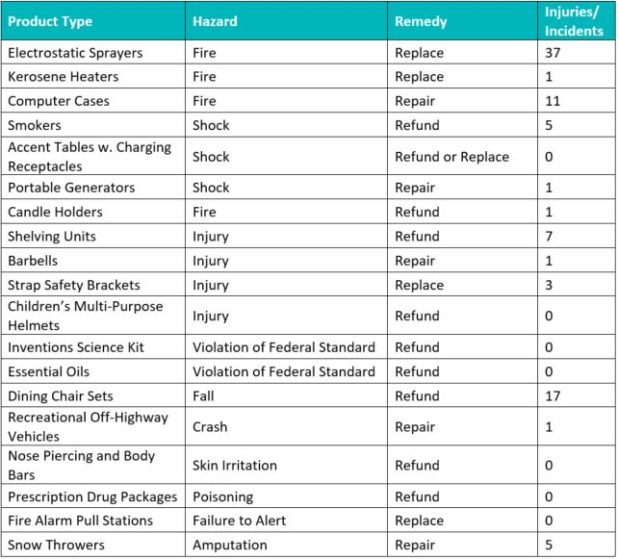
Total Recalls: 19
Hazards: Fire/Burn/Shock (7); Injury (4); Violation of Federal Standard (2); Fall (1); Crash (1); Skin Irritation (1); Poisoning (1); Failure to Alert (1); Amputation (1)
- Partner
Syed represents clients in connection with insurance coverage, reinsurance matters and other business litigation. Syed serves as the head of the firm’s insurance coverage practice. He has been admitted to the US Court of Appeals ...
- Partner
Kelly practices as a commercial and regulatory litigator on products liability and post M&A disputes and issues and serves as one of the firm’s Deputy General Counsel focusing on law firm ethics, conflicts, and risk management ...
- Partner
Geoff works closely with corporate policyholders and their directors and officers to resolve high-stakes insurance disputes. He leads the firm’s directors and officers (D&O) insurance and executive protection practice.
As a ...
- Counsel
Kevin is a commercial litigator focusing on insurance coverage disputes and counseling on behalf of policyholders. His educational background and prior experience as an insurance broker and advisor provide him with a deep ...
Search
Recent Posts
Categories
- Advertising & Marketing
- Bankruptcy
- Class Action
- Competition/Antitrust
- Consumer Protection
- Corporate Governance
- Environmental
- General
- Health Care
- Insurance
- IP
- Labor and Employment
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- News & Events
- Patent Infringement
- Patents
- Privacy & Cybersecurity
- Product Liability
- Real Estate
- Regulatory
- Technology & E-Commerce
Tags
- 29 C.F.R. § 785.48
- 396-r
- 3D Printer
- 3D Printing
- A. Todd Brown
- A.S. Research (ASR)
- Aaron P. Simpson
- Accountability
- Administrative Agencies
- Administrative Exemption
- Advertisers
- Advertising
- Advertising Claims
- Advertising Guidelines
- Advertising Idea
- Agency Guidance
- Agency Principles
- AI
- AI Interviewing Platforms
- AI Technology Reviews
- AIA
- Air
- Algorithmic Accountability Act
- Align
- Americans with Disabilities Act
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
- Andrea DeField
- Ann Marie Buerkle
- Annual Reports
- anti-aging
- Anti-Discrimination
- APEX Agreement
- Arbitration
- Arbitration Agreements
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- Arthritis
- Artificial Intelligence
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Asbestos
- Assembly Bill 51 (AB 51)
- ATDS
- Australia
- Auto-renewals
- Automatic Telephone Dialing System (ATDS)
- Automobile
- Automotive Body Parts Association (ABPA)
- Back to Work Emergency Ordinance
- biased endorsements
- Biden Administration
- Biometric Data
- Biometric Information
- Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA)
- BIPA
- Bitcoin
- Blockchain
- Board Diversity Disclosure
- Boards of Directors
- Bonuses
- Braille
- Branding
- Breach
- Breach of Contract
- Business Interruption
- Business Interruption Loss
- Businessowner’s Insurance
- California
- California Air Resources Board
- California Assembly Bill 2011
- California Employment Laws
- California Fair Employment and Housing Act
- California False Claims Act
- California Labor Code
- California Legislation
- California Senate Bill 6
- California’s Unfair Competition Law
- CAMS
- Canada
- Cannabis
- CARB
- CBD
- CBP
- CCPA
- Celebrity Endorsers
- Center for Disease Control (CDC)
- CFIUS
- CGL
- Chatbot
- Children’s Advertising
- Children’s Advertising Review Unit
- Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA)
- China
- Christopher J. Dufek
- Christopher W. Hasbrouck
- Christy Kiely
- CIPA
- Class Action
- Class Action Litigation
- Class Actions
- Clawback
- Click-to-Cancel
- Climate Change
- Climate Disclosure
- clinical trials
- Collective Action
- Colorado
- Commerce Clause
- Commercial General Liability
- Commercial Leasing
- Commercial Messaging
- Commercial Products
- Commercial Real Estate
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission
- Compensation
- Compliance
- Confidentiality
- Congress
- Connecticut
- Consent
- Consent Order
- Consumer Advertising
- Consumer Data
- Consumer Financial Protection Bureau
- Consumer Fraud
- consumer loyalty program
- Consumer Privacy
- Consumer Product Safety Act
- Consumer Products
- Consumer Products Safety Commission (CPSC)
- Consumer Protection
- Consumer Review Fairness Act of 2016 (CRFA)
- Consumer Reviews
- Consumer Rights
- Contamination
- Contract Law
- Controlled Substance Act
- Cookies
- Cookware
- COPPA
- Copyright
- Coronavirus/COVID-19
- Corp Fin
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Reporting
- Corporate Sustainability
- Corporate Transparency Act (CTA)
- Costco
- Counterfeit Goods
- Counterfeit Goods Seizure Act of 2019
- Court of International Trade
- CPPA
- CPRA
- CPSA
- CPSC
- Crack House Statute
- CRFA
- Crypto
- Cryptocurrency
- CSPA
- Cuba
- Currency
- Customs and Border Protection
- Cyber
- Cyber Coverage
- D&O
- D&O policies
- D. Andrew Quigley
- Damages
- Data Breach
- Davidson
- Deceptive Advertising
- DEI
- Delaware
- Delivery Drivers
- DEP
- Department of Agriculture
- Department of Justice
- Department of Labor
- Development Impact Fee
- Dietary Guidelines
- Digital Assets
- digital currency
- Disclosures
- Distribution
- Division of Corporation Finance
- Dodd-Frank
- DOJ
- DOL
- Duty to Defend
- Duty to Indemnify
- e-liquid products
- Eddie Bauer
- EEOC
- Electric Vehicles
- Eleventh Circuit
- Emily Burkhardt Vicente
- Employee Rights
- Endorsement
- Endorsement Guides
- Endorsement Notice
- Endorsements
- endorser monitoring requirements
- Enforcement
- Environmental Impact
- Environmental Protection Agency
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- EPA
- Epidemic
- ESG
- ESG Disclosure
- EU Regulation
- European Union
- European Unitary Patent
- EV Charging
- Exceptions
- Exclusions
- Executive Compensation Disclosure Rules
- Executive Order
- Executive Orders
- Exercise Machines
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR)
- FAA
- Fair Labor Standards Act
- Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)
- fair use
- False Advertising
- False Advertising Claims
- False Advertising Law
- False Claims Act
- Family Leave Policies
- FAR
- FCC
- FCRA
- FDA
- Federal Acquisition Regulations
- Federal Arbitration Act (FAA)
- Federal Communications Commission
- Federal Contractors
- Federal Contracts
- Federal District Court
- Federal Government Contractor
- Federal Government Shutdown
- Federal Trade Commission
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
- FFDCA
- FIFRA
- Fifth Circuit
- Final Rule
- Financial Technology
- FinCEN
- FinHub
- Fireworks
- First Amendment
- Fixing America’s Surface Transportation (FAST) Act
- Florida
- Florida House of Representatives (HB 963) and Florida Senate (SB 1670)
- Florida Legislature
- FLSA
- FLSA/Wage & Hour
- FMLA
- Food and Beverage Manufacturers
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
- Food Delivery
- Food Safety
- Form 10-K
- Formaldehyde Standards for Composite Wood Products Act of 2010
- fractional interests
- Franchise
- Frederic Chang
- Free Trials
- FTC
- FTC Act
- Gavin Newsom
- GDPR
- General Liability
- Geoffrey B. Fehling
- Georgia
- Gift Cards
- GoodRx
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley (GLB) Act
- Green
- Green Guides
- Greenhouse Gas
- Gun Safety
- Hart-Scott-Rodino
- Hart-Scott-Rodino (HSR)
- Hashtag
- Hawaii
- Health Care
- Health Claims
- Hedge Fund
- HIPAA
- hoverboards
- human capital
- Human Rights
- IEEPA
- Illinois
- Illinois Artificial Intelligence Video Interview Act (the Illinois Act)
- Illinois Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA)
- Independent Contractors
- Indiana
- Indoor Mall
- Influencer Marketing
- Infringement
- initial public offerings (IPOs)
- Injury
- Insurance
- Insurance Loss
- Insurance Provider
- Intellectual Property
- Intellectual Property Licenses in Bankruptcy Act
- Inter Partes Review
- Interest Rate
- International
- International Trade Commission
- International Trade Commission (ITC)
- Internet
- Inventorship
- investigation
- INVISALIGN
- Iowa
- IP
- IPR
- Ireland
- IT
- ITC
- iTERO
- Job Posting
- Junk Fees
- Katherine Miller
- Kurt A. Powell
- Kurt G. Larkin
- Labeling
- Labeling Requirements
- Labeling Rules
- Labor
- Labor Code Private Attorneys General Act of 2004 (PAGA)
- Labor Organizing
- Labor Unions
- Land Use
- Landlord
- Latin America
- Lautenberg Act
- Lawsuit Reform Alliance of New York (LRANY)
- Lead
- Lease
- Legislation
- Leveraged Loans
- Liability Insurance Policy
- Liberty Insurance Corporation
- Liberty Mutual Fire Insurance Company
- LIBOR Discontinuation
- liquidity
- Litigation
- Live Chat
- Lost Profits
- Lost Sales
- Louisiana
- M&A
- Made in the USA
- Made in USA
- MagicSleeve
- Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act
- Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act (MMWA)
- Maine
- Malcolm C. Weiss
- Manufacturing
- Marketing Claims
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Matthew T. McLellan
- Maya M. Eckstein
- MD&A
- Medtail
- Membership cancellation
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Metaverse
- MeToo Movement
- Mexico
- Michael J. Mueller
- Michael S. Levine
- microplastics
- Microplastics Litigation
- Minimum Wage
- Minnesota
- Minnesota Pollution Control Agency (MPCA)
- Misclassification
- Mislabeling
- Mission Product Holdings
- Missouri
- Mobile
- Mobile App
- Motoclick
- Multi-Family Housing Development
- Multi-Level Marketing Program (MLM)
- NAA
- NAD
- NASA
- Nasdaq
- National Advertising Division
- National Advertising Division (NAD)
- National Advertising Review Board
- National Labor Relations Act
- National Labor Relations Board
- National Products Inc.
- National Retail Federation
- Natural Disaster
- Nebraska
- Negligence Claims
- Neil K. Gilman
- Network Outage
- Nevada
- New Jersey
- New York
- New York City Department of Consumer and Worker Protection
- NHTSA
- NIL rights
- Ninth Circuit
- NLRA
- NLRB
- no-action request
- Non-Compete
- Non-Exempt
- Non-Exempt Employees
- non-fungible token (NFT)
- North Carolina
- Nutrition Labels
- Obama Administration
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
- Occurrence
- Office of Labor Standards Enforcement
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Online Cash Providers
- Online Retailer
- Online Reviews
- Opinion Letters
- Opioids
- Oregon
- Overboarding
- Overtime
- Overtime Exemptions
- Ownership
- Packaging
- PAGA
- Pandemic
- Patent
- Patent Infringement
- Patents
- Paul T. Moura
- Pay Equity
- Pay Ratio
- Pay Transparency
- Pay-To-Play Rankings
- Penalty
- Pennsylvania
- Personal and Advertising Injury
- Personal Data
- Personal Information
- Personally Identifiable Information
- Pesticides
- PFAS
- Physical Loss or Damage
- Policy
- price gouging
- Primary and Umbrella Policies
- Privacy
- Privacy Guidelines
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Protections
- Procurement
- Product Liability
- Product Packaging
- Prohibition on Sale
- Property Insurance
- Property Rights
- Proposed Legislation
- Proposition 65
- Proxy Access
- proxy materials
- Proxy Statements
- PTAB
- PTO
- Public Companies
- Purdue Pharma
- Randall S. Parks
- Ransomware
- Real Estate
- Recall
- Recalls
- Recording
- Regulation
- Regulation S-K
- Restaurants
- Restrictive Covenants
- Retail
- Retail Developers
- Retail Development
- Retail Industry Leaders Association
- Retail Litigation Center
- Retail Year in Review
- Rounding
- Rulemaking
- Ryan A. Glasgow
- Sales Tax
- Salesforce
- SD8 coins
- SEC
- SEC Disclosure
- Second Circuit
- Section 337
- Section 365
- Secure and Fair Enforcement Banking Act of 2019 (“SAFE Banking Act”)
- Securities
- Securities and Exchange Commission
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Securities Exchange Commission
- security checks
- Senate
- Senate Data Handling Report
- Sergio F. Oehninger
- Service Contract Act (SCA)
- Service Interruption
- Service Provider
- SHARE
- Shareholder
- Shareholder Proposals
- Sign-In Wrap Agreement
- Slogan
- Smart Contracts
- SNAP
- Social Media
- Social Media Influencers
- Software
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Special purpose acquisition companies (SPACs)
- Sponsors and Gifting
- Sponsorship
- State Attorneys General
- State Law
- State Legislation
- Store Closures
- Subscription Services
- Substantiation
- Substantiation Notice
- Supplier
- Supply Chain
- Supply contracts
- Supreme Court
- Sustainability
- Syed S. Ahmad
- Synovia
- Targeted Advertising
- Tariff
- Tax
- TCCWNA
- TCPA
- Technology
- Technology Innovation
- Telemarketing
- Telephone Consumer Protection Act
- Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA)
- Tempnology LLC
- Tenant
- Tennessee
- Terms and Conditions
- Texas
- The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)
- Third-Party
- Thomas R. Waskom
- Title VII
- Tokenization
- Tokens
- Toxic Chemicals
- Toxic Substances Control Act
- Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA)
- Trade Dress
- Trademark
- Trademark Infringement
- Trademark Trial and Appeal Board (TTAB)
- TransUnion
- Travel
- Trump Administration
- TSCA
- TSCA Title VI
- U.S. Department of Justice
- U.S. Department of Labor
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- U.S. House of Representatives
- U.S. Patent and Trademark Office
- Ultra-Processed Foods
- Umbrella Liability
- Unfair and Deceptive Use
- Union
- Union Organizing
- United Specialty Insurance Company
- Unmanned Aircraft
- Unruh Civil Rights Act
- UPSTO
- US Chamber of Commerce
- US Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
- US International Trade Commission (ITC)
- US Origin Claims
- US Patent and Trademark Office
- US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO)
- US Supreme Court
- USDA
- USPTO
- Utah
- Varidesk
- Vendor
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Emissions
- W. Jeffery Edwards
- Wage and Hour
- Wage-And-Hour
- Walter J. Andrews
- Warning Labels
- Warranties
- Warranty
- Washington
- Washington DC
- WCAG
- Web Accessibility
- Website
- Website Accessibility
- Weight Loss
- Wiretap
- Wiretapping
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Wyoming
- Year In Review
- Zoning
- Zoning Conversion
- Zoning Ordinances
- Zoning Regulations
Authors
- Gary A. Abelev
- Alexander Abramenko
- Yaniel Abreu
- Christian S. Adams
- Syed S. Ahmad
- Brandon Bell
- Fawaz A. Bham
- Michael J. “Jack” Bisceglia
- Jennifer L. Bloom
- Jeremy S. Boczko
- Brian J. Bosworth
- Shannon S. Broome
- Samuel L. Brown
- Tyler P. Brown
- Melinda Brunger
- Jimmy Bui
- M. Brett Burns
- Olivia G. Bushman
- Matthew J. Calvert
- Grant H. Cokeley
- Abigail Contreras
- Eric S. Crusius
- Christopher J. Cunio
- Alexandra B. Cunningham
- Merideth Snow Daly
- Timothy G. Decker
- Andrea DeField
- John J. Delionado
- Stephen P. Demm
- Mayme Donohue
- Christopher J. Dufek
- Robert T. Dumbacher
- M. Kaylan Dunn
- Chloe Dupre
- Frederick R. Eames
- Maya M. Eckstein
- Rob Edwards
- Tara L. Elgie
- Clare Ellis
- Latosha M. Ellis
- Juan C. Enjamio
- Kelly L. Faglioni
- Ozzie A. Farres
- Geoffrey B. Fehling
- Hannah Flint
- Erin F. Fonté
- Kevin E. Gaunt
- Jane M. Geiger
- Andrew G. Geyer
- Armin Ghiam
- Neil K. Gilman
- Ryan A. Glasgow
- Tonya M. Gray
- Elisabeth R. Gunther
- Steven M. Haas
- Kevin Hahm
- Jason W. Harbour
- Jeffrey L. Harvey
- Christopher W. Hasbrouck
- Eileen Henderson
- Gregory G. Hesse
- Kirk A. Hornbeck
- Mark Ingram
- Jamie Zysk Isani
- Nicole R. Johnson
- Roland M. Juarez
- James A. Kennedy, II
- Suzan Kern
- Jason J. Kim
- Scott H. Kimpel
- Elizabeth King
- Andrew S. Koelz
- Leslie W. Kostyshak
- Perie Reiko Koyama
- Torsten M. Kracht
- Kurt G. Larkin
- Tyler S. Laughinghouse
- Gerry Leone
- Michael S. Levine
- Ashley Lewis
- Abigail M. Lyle
- Maeve Malik
- Eric R. Markus
- John Gary Maynard, III
- Aubrianna L. Mierow
- Gray Moeller
- Reilly C. Moore
- Michael D. Morfey
- Ann Marie Mortimer
- Michael J. Mueller
- J. Drei Munar
- Matthew Nigriny
- Michael A. Oakes
- Justin F. Paget
- Christopher M. Pardo
- Randall S. Parks
- J. Steven Patterson
- Katherine C. Pickens
- Gregory L. Porter
- Robert T. Quackenboss
- D. Andrew Quigley
- Michael Reed
- Shawn Patrick Regan
- Jonathan D. Reichman
- Kelli Regan Rice
- Patrick L. Robson
- Amber M. Rogers
- Natalia San Juan
- Katherine P. Sandberg
- Arthur E. Schmalz
- Daniel G. Shanley
- Madison W. Sherrill
- Kevin V. Small
- J.R. Smith
- Bennett Sooy
- Brian T. Stansbury
- Daniel Stefany
- Hak Stepanyan
- Javaneh S. Tarter
- Paige Van Oosten
- Jessica N. Vara
- Emily Burkhardt Vicente
- Mark R. Vowell
- Gregory R. Wall
- Thomas R. Waskom
- Malcolm C. Weiss
- Holly H. Williamson
- Samuel Wolff
- Jingyi “Alice” Yao
- Jessica G. Yeshman




